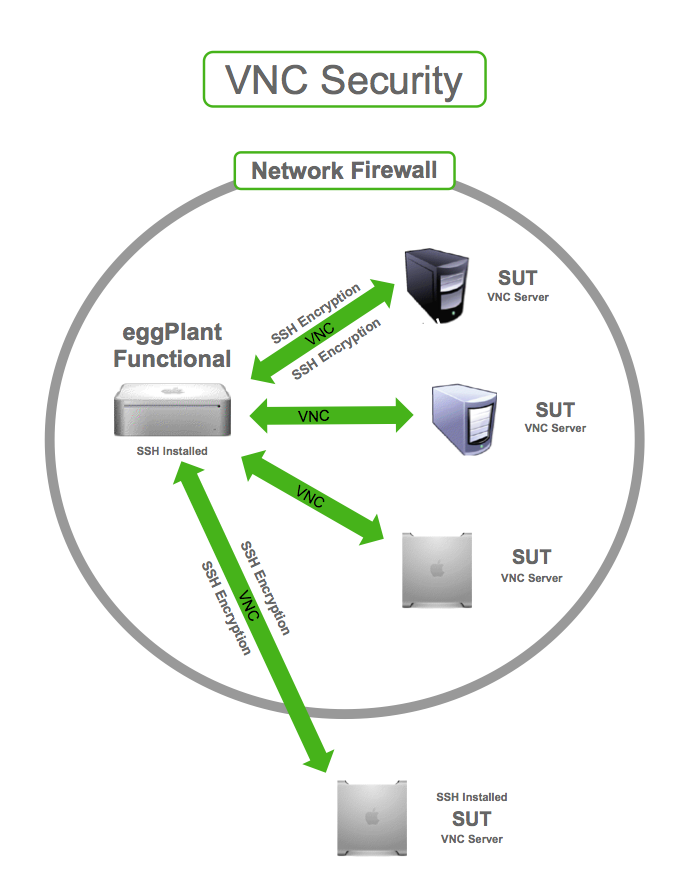
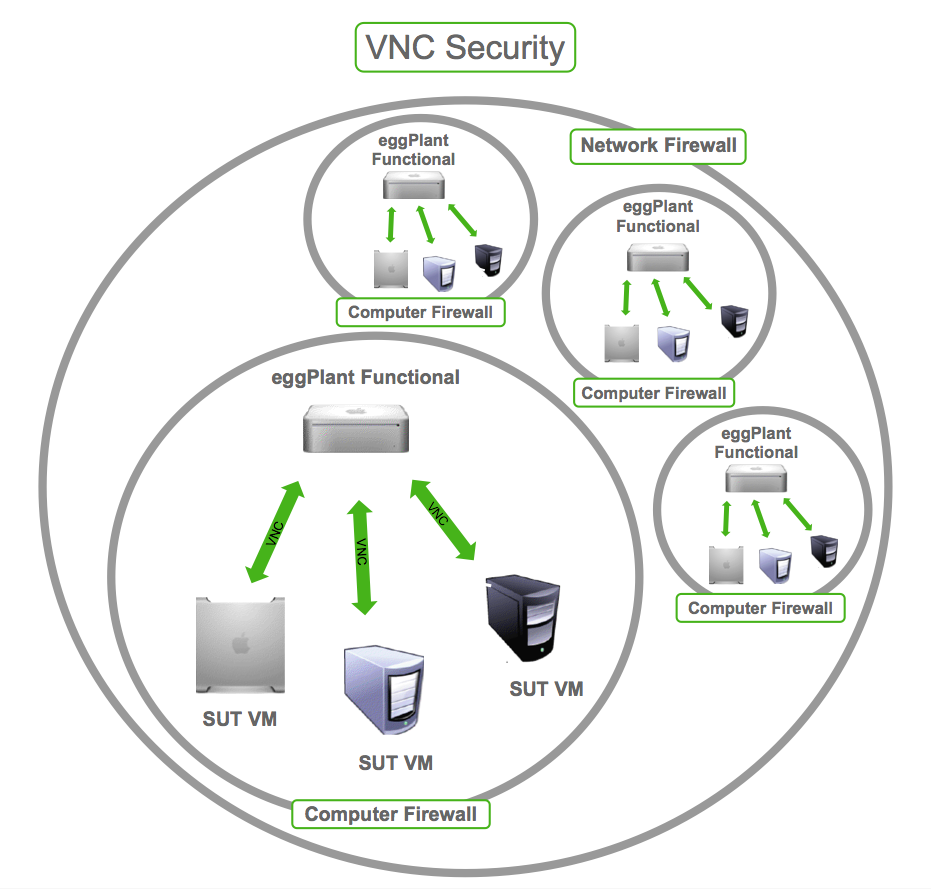
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a widely used technology that allows users to remotely control another computer. However, VNC security issues have become a growing concern for individuals and organizations alike. As remote work and remote access continue to grow, the need for robust VNC security measures has never been more critical. Understanding these vulnerabilities and implementing best practices can help protect your data and network from potential threats.
VNC has become an essential tool for IT professionals and remote workers, providing a convenient way to access and manage computers from anywhere in the world. However, with convenience comes risk. VNC security issues can expose sensitive data and leave networks vulnerable to cyberattacks. This article will explore the risks associated with VNC, discuss best practices for securing your connections, and provide actionable advice to mitigate these threats.
Whether you're a small business owner, an IT administrator, or an individual user, understanding VNC security risks is crucial to protecting your digital assets. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the common vulnerabilities, best practices for securing VNC connections, and tools to help you stay safe while using this powerful technology.
Read also:Mastering Property Management Hvac Vendors A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction to VNC
- Common VNC Security Issues
- Vulnerabilities in VNC
- Securing VNC Connections
- Best Practices for VNC Security
- Tools for Enhancing VNC Security
- VNC Security and Regulatory Compliance
- VNC Security for Remote Work
- Case Studies of VNC Security
- Future of VNC Security
- Conclusion
Introduction to VNC
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a graphical desktop sharing system that allows users to remotely control another computer over a network connection. VNC uses the Remote Framebuffer Protocol (RFB) to transmit keyboard and mouse events between machines. While VNC offers numerous benefits, such as remote troubleshooting and file sharing, it also comes with inherent security risks that must be addressed.
VNC is widely used in various industries, including IT support, education, and healthcare. Its ability to provide real-time access to remote systems makes it an invaluable tool for many organizations. However, as reliance on remote access technologies grows, so does the importance of ensuring VNC security.
Understanding the basics of VNC and its underlying protocols is essential for identifying potential vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate security measures. This section will cover the fundamentals of VNC, its applications, and why securing VNC connections is critical in today's digital landscape.
Common VNC Security Issues
Weak Authentication
One of the most common VNC security issues is weak authentication. Many users rely on simple passwords or fail to implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), leaving their VNC connections vulnerable to unauthorized access. According to a report by cybersecurity firm Avast, over 60% of VNC connections are protected by weak or default passwords.
Unencrypted Connections
Another significant issue is the use of unencrypted VNC connections. Without encryption, sensitive data transmitted over VNC can be intercepted by attackers. This vulnerability is particularly concerning for organizations handling confidential or personal information.
Firewall Misconfigurations
Firewall misconfigurations can also lead to VNC security issues. Improperly configured firewalls may expose VNC ports to the internet, making them an easy target for hackers. Regularly reviewing and updating firewall settings is crucial to maintaining VNC security.
Read also:Devil Jin Tekken 8 Customization A Comprehensive Guide For Fans
Vulnerabilities in VNC
VNC systems are not immune to vulnerabilities, and several known issues have been identified over the years. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems or steal sensitive data. Below are some of the most notable VNC vulnerabilities:
- Buffer Overflow Vulnerabilities: Certain VNC implementations have been found to be susceptible to buffer overflow attacks, which can allow attackers to execute arbitrary code.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Without proper encryption, VNC connections are vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks, where attackers intercept and alter communications between systems.
- Default Credentials: Many VNC servers come with default credentials that are rarely changed, making them easy targets for brute-force attacks.
Staying informed about these vulnerabilities and applying necessary patches and updates is essential for maintaining VNC security.
Securing VNC Connections
Implementing Encryption
Encrypting VNC connections is one of the most effective ways to enhance security. By using protocols such as TLS or SSH tunneling, you can protect sensitive data from interception. Many modern VNC clients and servers support encryption, making it easier than ever to secure your connections.
Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access. This can include something the user knows (password), something the user has (a mobile device), or something the user is (biometric data). Enabling MFA for VNC connections significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Restricting Access
Restricting access to VNC servers through IP whitelisting or network segmentation can further enhance security. By limiting who can connect to your VNC servers, you reduce the attack surface and minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Best Practices for VNC Security
Implementing best practices is key to ensuring VNC security. Below are some actionable tips to help you protect your VNC connections:
- Use strong, unique passwords for all VNC accounts.
- Regularly update VNC software to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Monitor VNC activity logs for suspicious behavior.
- Limit VNC access to trusted networks or IP addresses.
- Disable unused or unnecessary VNC features to reduce risk.
By following these best practices, you can significantly improve the security of your VNC connections and protect your data from potential threats.
Tools for Enhancing VNC Security
Firewall Software
Firewall software can help protect VNC servers by controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic. Tools like iptables (for Linux) or Windows Firewall provide robust protection against unauthorized access.
Encryption Tools
Encryption tools such as OpenSSL or stunnel can be used to secure VNC connections. These tools provide strong encryption protocols to protect data in transit.
Monitoring Tools
Monitoring tools like Nagios or Zabbix can help track VNC activity and alert administrators to potential security incidents. Regular monitoring is essential for maintaining VNC security.
VNC Security and Regulatory Compliance
VNC security is not only important for protecting data but also for ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Organizations in industries such as healthcare, finance, and government must adhere to strict data protection regulations, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS. Failing to secure VNC connections can result in fines, legal action, and reputational damage.
To ensure compliance, organizations should implement robust VNC security measures, regularly audit their systems, and train employees on best practices. Staying informed about regulatory requirements and adapting security measures accordingly is crucial for maintaining compliance.
VNC Security for Remote Work
With the rise of remote work, VNC security has become even more critical. Remote workers often rely on VNC to access company resources, making it essential to secure these connections. Employers should provide employees with secure VNC tools, enforce strong authentication policies, and regularly educate staff on cybersecurity best practices.
Implementing a secure VNC setup for remote work requires careful planning and execution. Organizations should consider using virtual private networks (VPNs) to further enhance security and ensure all remote connections are protected.
Case Studies of VNC Security
Several high-profile incidents highlight the importance of VNC security. For example, in 2019, researchers discovered over 70,000 unsecured VNC servers exposed to the internet. These servers contained sensitive information, including personal data and financial records, leaving them vulnerable to exploitation.
Another notable case involved a healthcare provider whose VNC server was breached, resulting in the exposure of patient data. This incident underscores the need for robust VNC security measures, especially in industries handling sensitive information.
Future of VNC Security
As technology continues to evolve, so do the methods used by attackers to exploit VNC vulnerabilities. The future of VNC security will likely involve advancements in encryption, authentication, and monitoring technologies. Additionally, the adoption of zero-trust architectures and AI-driven threat detection systems will play a significant role in enhancing VNC security.
Organizations and individuals must stay informed about emerging threats and adopt proactive security measures to protect their VNC connections. Investing in cutting-edge security tools and training employees on best practices will be crucial in securing VNC in the years to come.
Conclusion
VNC security issues are a growing concern for individuals and organizations relying on remote access technologies. By understanding the risks associated with VNC and implementing best practices, you can significantly improve the security of your connections and protect your data from potential threats.
We encourage readers to take action by reviewing their VNC setups, updating software, and implementing encryption and authentication measures. Additionally, sharing this article with colleagues and exploring other resources on VNC security can help spread awareness and promote safer practices.
Stay vigilant, stay informed, and ensure your VNC connections are as secure as possible. Together, we can mitigate VNC security risks and create a safer digital environment for everyone.