In the era of interconnected devices, Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way we interact with technology. One critical aspect of managing IoT devices is through secure shell (SSH) login using command-line interface (CLI) commands. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced professional, understanding IoT SSH login CLI commands is essential for efficient device management.
As IoT continues to expand, the need for secure and efficient device management becomes increasingly important. SSH provides a secure channel for remote access, ensuring that your IoT devices remain protected from unauthorized access. This article will delve into the intricacies of IoT SSH login CLI commands, offering practical insights and actionable tips.
By mastering these commands, you can enhance your device management capabilities while ensuring robust security measures. Whether you're configuring a smart home system or managing industrial IoT networks, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to succeed.
Read also:Lisa Marie Presley The Legacy Of A Musical Icon
Table of Contents
- Introduction to SSH and Its Role in IoT
- Basic IoT SSH Login CLI Commands
- Advanced IoT SSH Commands for Device Management
- Security Best Practices for IoT SSH Login
- Troubleshooting Common IoT SSH Issues
- Real-World Use Cases of IoT SSH Login
- Essential Tools and Software for IoT SSH
- Performance Optimization for IoT SSH Connections
- Automating IoT SSH Processes with CLI Commands
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to SSH and Its Role in IoT
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol that facilitates secure communication between devices over an unsecured network. In the context of IoT, SSH plays a pivotal role in enabling remote access and management of IoT devices. By leveraging IoT SSH login CLI commands, administrators can securely connect to devices, execute commands, and manage configurations.
SSH ensures data integrity and confidentiality by encrypting all communications between the client and server. This makes it an ideal solution for IoT environments where security is paramount. Whether you're managing a fleet of smart sensors or monitoring industrial equipment, understanding SSH is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency.
As IoT networks grow in complexity, the ability to efficiently manage devices using SSH becomes increasingly important. This section will explore the fundamental principles of SSH and its significance in IoT ecosystems.
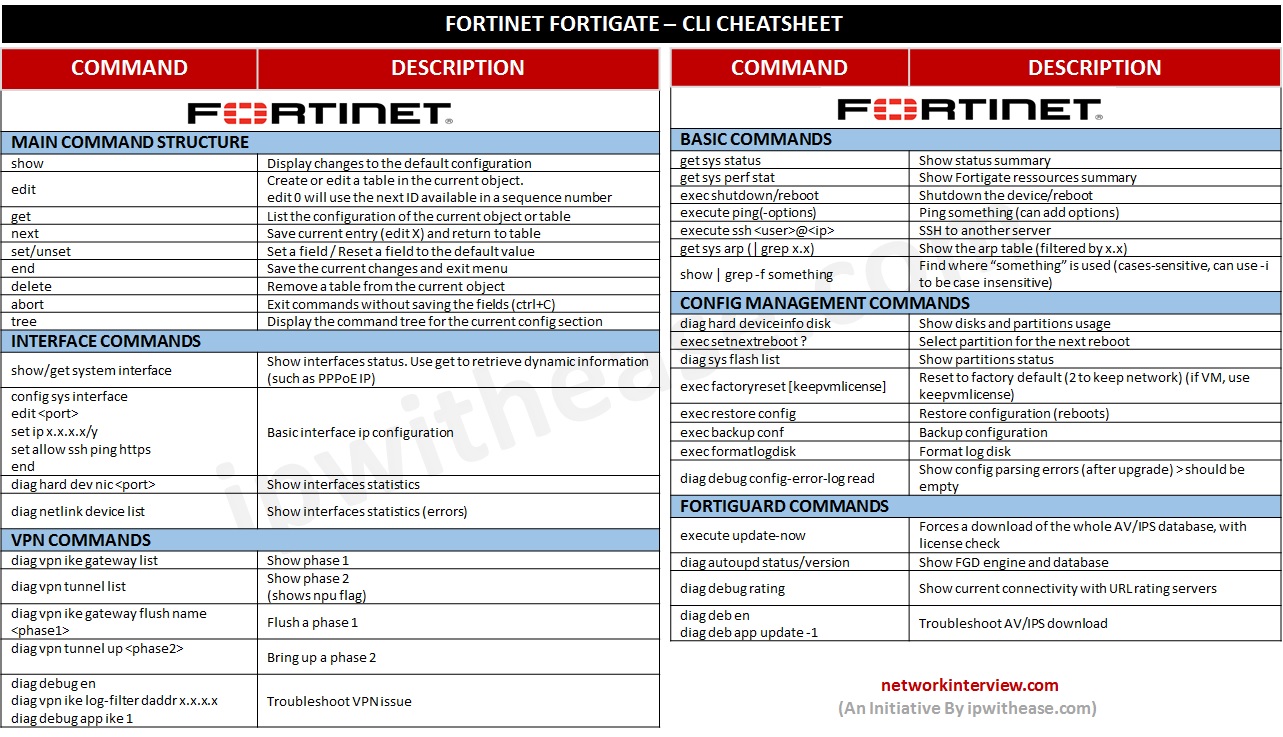
Basic IoT SSH Login CLI Commands
Before diving into advanced configurations, it's essential to familiarize yourself with the basic IoT SSH login CLI commands. These commands form the foundation of device management and are indispensable for day-to-day operations.
Connecting to an IoT Device
Establishing a secure connection to an IoT device is the first step in managing it via SSH. The following command demonstrates how to connect to a device:
ssh username@hostname
Replace username with your login credentials and hostname with the IP address or domain name of the IoT device.
Read also:Cindy Williams Cause Of Death A Detailed Look Into Her Life And Legacy
Basic Navigation and File Management
Once connected, you can use CLI commands to navigate the file system and manage files. Here are some commonly used commands:
ls- List directory contentscd- Change directorymkdir- Create a new directoryrm- Remove files or directories
These commands allow you to efficiently manage files and directories on your IoT devices.
Advanced IoT SSH Commands for Device Management
Once you've mastered the basics, it's time to explore advanced IoT SSH commands that enhance device management capabilities. These commands enable you to perform complex tasks and automate workflows.
Configuring SSH Keys for Passwordless Login
Using SSH keys eliminates the need for password-based authentication, enhancing security and convenience. Follow these steps to set up SSH keys:
ssh-keygen -t rsa- Generate an RSA key pairssh-copy-id username@hostname- Copy the public key to the remote device
This setup ensures seamless access to your IoT devices without compromising security.
Monitoring System Resources
Monitoring system resources is critical for maintaining optimal performance. Use the following commands to monitor CPU, memory, and disk usage:
top- Display real-time system processesfree -m- Show memory usage in megabytesdf -h- Display disk usage in a human-readable format
These commands provide valuable insights into the health of your IoT devices.
Security Best Practices for IoT SSH Login
Securing your IoT devices is paramount, and SSH provides several mechanisms to enhance security. By adhering to best practices, you can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Disable Root Login
Disabling root login reduces the attack surface by preventing direct access to administrative privileges. To disable root login, edit the SSH configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config- Set
PermitRootLogin no - Restart the SSH service
Implement Firewall Rules
Configuring firewall rules ensures that only authorized connections are allowed. Use tools like iptables or ufw to define access policies:
sudo ufw allow sshsudo ufw enable
These steps help protect your IoT devices from malicious attacks.
Troubleshooting Common IoT SSH Issues
Despite its robustness, SSH can sometimes encounter issues. Understanding common problems and their solutions is essential for maintaining smooth operations.
Connection Timeouts
Connection timeouts often occur due to network latency or misconfigured settings. To resolve this issue:
- Check network connectivity
- Verify SSH service status
- Adjust connection parameters in the SSH configuration file
Permission Denied Errors
Permission denied errors typically arise from incorrect permissions or mismatched keys. To address this issue:
- Verify file permissions
- Ensure correct key pair is used
- Check ownership of authorized_keys file
By systematically troubleshooting these issues, you can restore functionality quickly.
Real-World Use Cases of IoT SSH Login
IoT SSH login CLI commands find applications across various industries, enabling efficient device management and automation. Here are some real-world use cases:
Smart Home Automation
SSH allows homeowners to remotely manage smart home devices, ensuring convenience and security. From controlling lighting systems to monitoring security cameras, SSH streamlines the management process.
Industrial IoT Networks
In industrial settings, SSH is used to monitor and manage critical infrastructure. Engineers can access remote sensors, configure settings, and troubleshoot issues without physical presence.
These use cases highlight the versatility and importance of SSH in modern IoT ecosystems.
Essential Tools and Software for IoT SSH
Several tools and software enhance the functionality of IoT SSH login CLI commands, making device management more efficient. Here are some notable options:
SSH Clients
- OpenSSH - A widely used SSH client for Linux and Unix systems
- PuTTY - A popular SSH client for Windows users
Automation Tools
- Ansible - A powerful automation tool for managing SSH-based workflows
- Paramiko - A Python library for SSH protocol implementation
These tools provide additional capabilities, enabling users to streamline their workflows.
Performance Optimization for IoT SSH Connections
Optimizing SSH performance ensures faster and more reliable connections, enhancing the user experience. Here are some strategies to improve performance:
Compression
Enabling compression reduces data transfer times, making SSH sessions more efficient. Add the following line to your SSH configuration file:
Compression yes
Keep-Alive Settings
Configuring keep-alive settings prevents idle connections from being dropped. Use the following parameters:
ServerAliveInterval 60ServerAliveCountMax 3
These optimizations ensure stable and efficient SSH connections.
Automating IoT SSH Processes with CLI Commands
Automation simplifies repetitive tasks, saving time and reducing errors. By leveraging CLI commands, you can automate various IoT SSH processes. Here are some examples:
Scripting with Bash
Bash scripts enable you to automate SSH-based tasks, such as device monitoring and data collection. Create a script with the following commands:
ssh user@hostname 'command'scp file user@hostname:/path/to/destination
Scheduling with Cron
Cron allows you to schedule automated tasks, ensuring regular execution of SSH commands. Add a cron job with the following syntax:
crontab -e- Add the desired command and schedule
Automation empowers users to manage IoT devices more effectively.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Mastering IoT SSH login CLI commands is essential for efficient device management in the IoT ecosystem. By understanding the fundamentals, exploring advanced configurations, and adhering to security best practices, you can enhance your capabilities as an IoT professional. This comprehensive guide has provided insights into various aspects of SSH, equipping you with the knowledge needed to succeed.
We encourage you to take the following steps:
- Practice the commands discussed in this article
- Explore additional resources for further learning
- Share your experiences and insights in the comments section
Thank you for reading, and we hope this guide proves valuable in your IoT journey. For more informative content, explore our other articles and stay updated with the latest trends in technology.