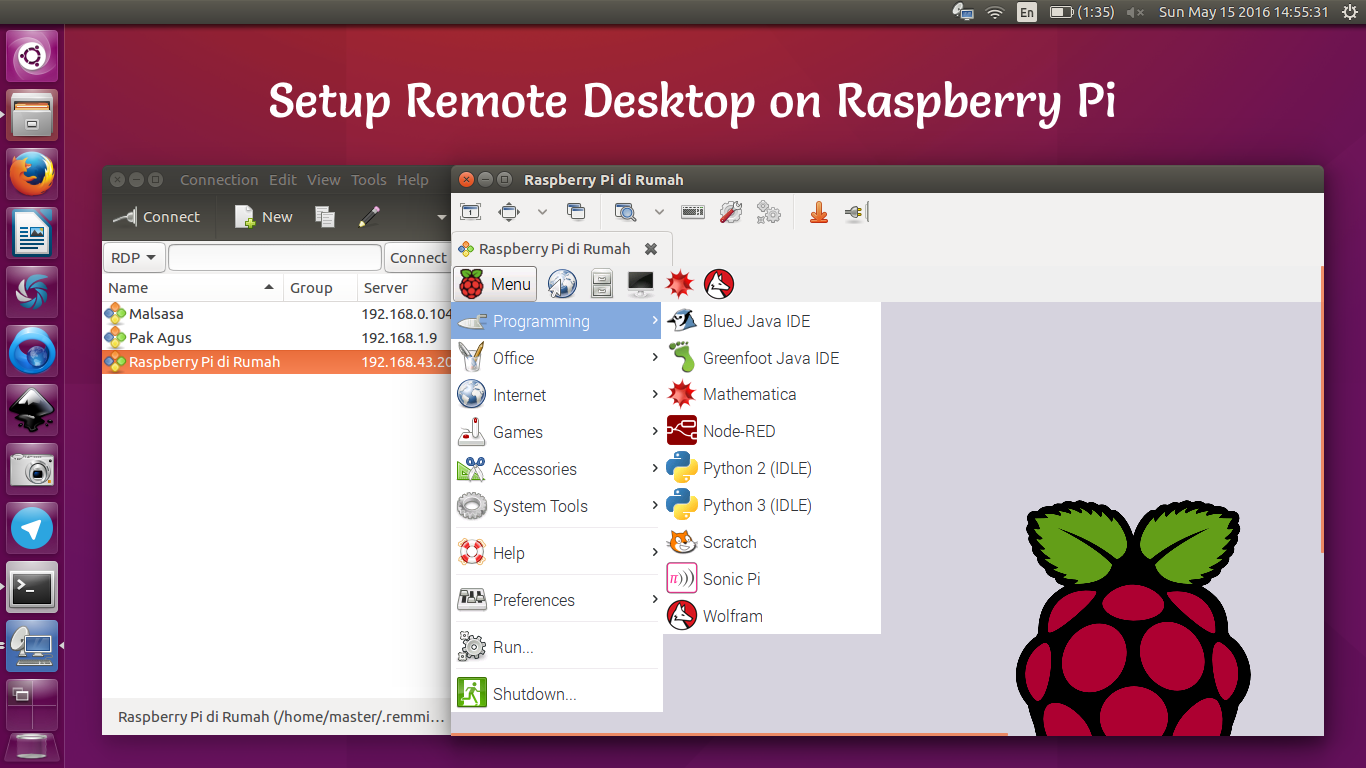
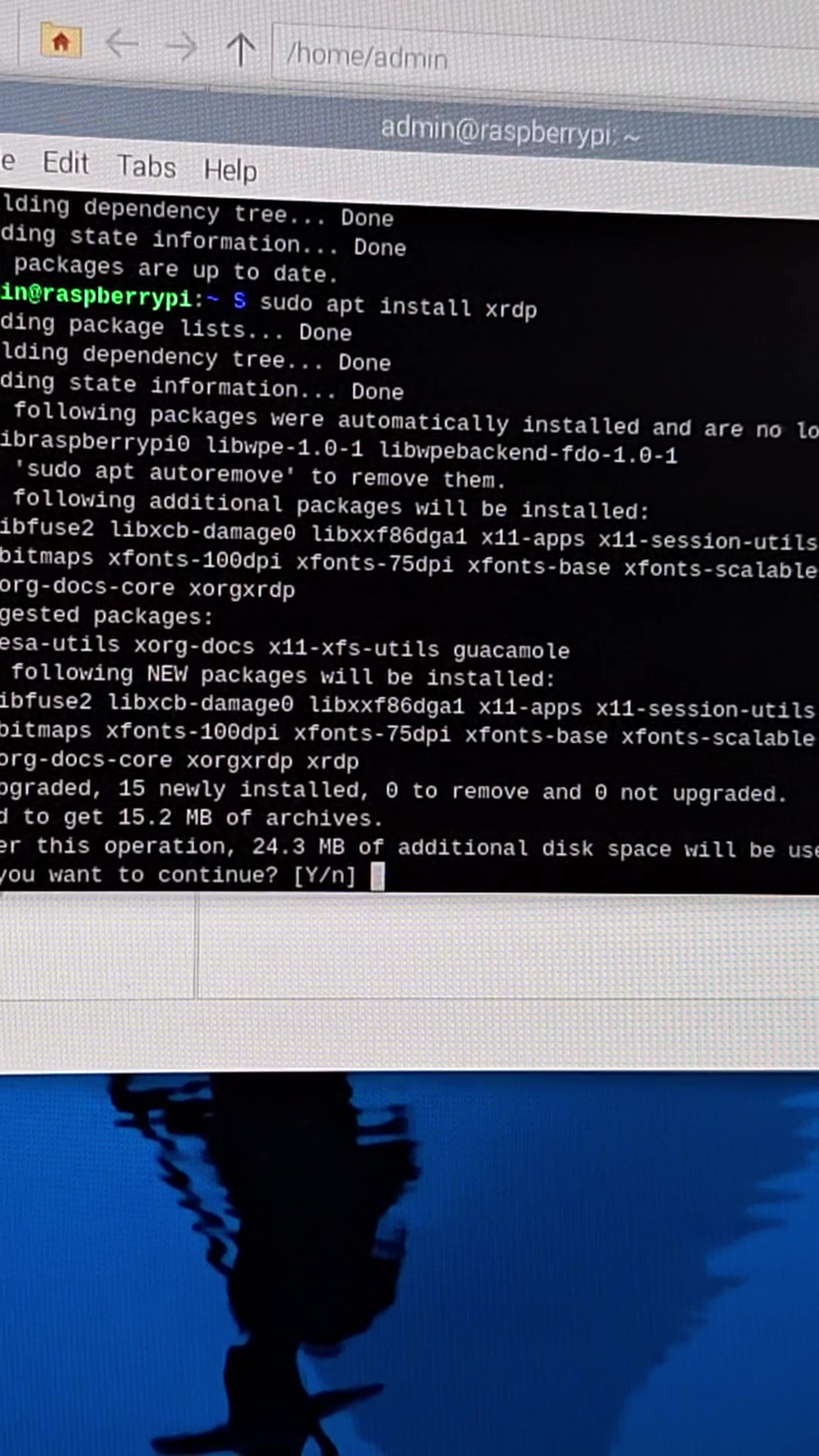
Remote access to your Raspberry Pi can significantly enhance your productivity and flexibility when managing projects or devices. Whether you're a developer, hobbyist, or IT professional, knowing how to enable remote access is a valuable skill. In this article, we'll explore the step-by-step process of setting up remote access for your Raspberry Pi, ensuring secure and reliable connectivity.
As technology evolves, remote access has become an essential feature for managing devices like the Raspberry Pi. This compact yet powerful device is widely used for various applications, from home automation to server hosting. However, without proper remote access configuration, its full potential cannot be utilized effectively.
This guide aims to provide you with all the necessary information to enable remote access on your Raspberry Pi. By following the steps outlined here, you can confidently connect to your Raspberry Pi from anywhere, ensuring seamless operation and maintenance of your projects.
Read also:Lisa Marie Presley The Legacy Of A Musical Icon
Why Enable Remote Access Raspberry Pi?
Enabling remote access for your Raspberry Pi offers numerous advantages, including increased flexibility, convenience, and efficiency. Here are some reasons why remote access is essential:
- Remote Management: You can manage your Raspberry Pi without being physically present, allowing you to work from any location.
- Cost-Effective: Eliminate the need for additional hardware or travel expenses when troubleshooting or updating your device.
- Scalability: Ideal for managing multiple Raspberry Pi devices simultaneously, especially in large-scale projects or server environments.
- Security: With proper configuration, remote access can be secure, protecting your device from unauthorized access.
Daftar Isi
- Why Enable Remote Access Raspberry Pi?
- Pre-requisites for Setting Up Remote Access
- Setting Up SSH for Raspberry Pi
- Configuring VNC for Remote Access
- Network Configuration for Remote Access
- Adjusting Firewall Settings for Security
- Port Forwarding for External Access
- Using Dynamic DNS for Easy Access
- Security Tips for Remote Access
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
Pre-requisites for Setting Up Remote Access
Before enabling remote access for your Raspberry Pi, ensure you have the following prerequisites in place:
- Raspberry Pi device with Raspbian or any compatible operating system installed.
- A stable internet connection for both the Raspberry Pi and the remote device.
- Basic knowledge of Linux command-line operations.
- Access to a router or modem for network configuration.
Having these prerequisites will ensure a smooth setup process and avoid potential issues during configuration.
Setting Up SSH for Raspberry Pi
SSH (Secure Shell) is one of the most common methods for enabling remote access to a Raspberry Pi. It provides a secure and encrypted connection, allowing you to manage your device remotely via the command line.
To enable SSH on your Raspberry Pi:
- Boot your Raspberry Pi and log in to the operating system.
- Open the terminal and type the following command:
sudo raspi-config
Read also:Is Katie Hopkins Married Exploring The Personal Life And Journey Of A Controversial Figure
In the configuration menu, navigate to "Interfacing Options" and select "SSH". Choose "Enable" to activate the SSH service.
Verifying SSH Status
After enabling SSH, you can verify its status by running the following command:
sudo service ssh status
If the service is active, you will see a message confirming that SSH is running.
Configuring VNC for Remote Access
While SSH is ideal for command-line access, VNC (Virtual Network Computing) allows you to access the graphical user interface (GUI) of your Raspberry Pi remotely.
Installing VNC Server
To set up VNC on your Raspberry Pi, follow these steps:
- Open the terminal and install the VNC server by typing:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install realvnc-vnc-server realvnc-vnc-viewer
- After installation, enable the VNC service by navigating to "Preferences"> "Raspberry Pi Configuration"> "Interfaces" and selecting "Enable" for VNC.
Connecting via VNC Client
To connect to your Raspberry Pi remotely, download and install the VNC Viewer application on your computer or mobile device. Enter the IP address of your Raspberry Pi and log in using your credentials.
Network Configuration for Remote Access
Proper network configuration is crucial for enabling remote access to your Raspberry Pi. Ensure that your device is connected to the same local network as your remote device. Additionally, note the IP address of your Raspberry Pi, which is required for establishing a connection.
To find the IP address, run the following command in the terminal:
hostname -I
This command will display the IP address of your Raspberry Pi, which you can use for remote connections.
Adjusting Firewall Settings for Security
Firewall settings play a vital role in securing your Raspberry Pi during remote access. By default, most firewalls block incoming connections, so you need to configure them to allow SSH and VNC traffic.
To adjust firewall settings on your Raspberry Pi:
- Install the UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) package by running:
sudo apt install ufw
- Allow SSH and VNC ports by executing the following commands:
sudo ufw allow 22
sudo ufw allow 5900
- Enable the firewall with the command:
sudo ufw enable
Port Forwarding for External Access
If you want to access your Raspberry Pi from outside your local network, you need to configure port forwarding on your router. This process involves directing external traffic to the internal IP address of your Raspberry Pi.
Steps for port forwarding:
- Log in to your router's administrative interface using a web browser.
- Locate the "Port Forwarding" or "NAT" settings section.
- Add a new rule, specifying the external port (e.g., 22 for SSH) and the internal IP address of your Raspberry Pi.
- Save the settings and test the connection from an external network.
Using Dynamic DNS for Easy Access
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) simplifies remote access by assigning a static domain name to your Raspberry Pi, even if its IP address changes. Services like No-IP or DuckDNS provide free DDNS solutions that you can integrate with your device.
To set up DDNS:
- Create an account with a DDNS provider and register a domain name.
- Install the DDNS client on your Raspberry Pi by following the provider's instructions.
- Configure the client to update the domain name with your current IP address automatically.
Security Tips for Remote Access
Securing your Raspberry Pi is essential when enabling remote access. Follow these best practices to protect your device:
- Use Strong Passwords: Create complex passwords for your Raspberry Pi user accounts and avoid using default credentials.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification step during login.
- Update Regularly: Keep your operating system and applications up to date to patch vulnerabilities.
- Limit Access: Restrict remote access to specific IP addresses or networks if possible.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
During the setup process, you may encounter some common issues. Here are solutions to help you resolve them:
- Connection Refused: Ensure that SSH or VNC services are running and that the correct IP address is used.
- Firewall Blocks Traffic: Verify that the necessary ports are open in your firewall settings.
- Port Forwarding Not Working: Double-check the router configuration and ensure that the external port matches the internal port.
- DDNS Not Updating: Restart the DDNS client or check the provider's status page for any outages.
Kesimpulan
Enabling remote access for your Raspberry Pi opens up endless possibilities for managing and interacting with your device from anywhere. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently set up SSH and VNC, configure network settings, and ensure security for your Raspberry Pi.
We encourage you to share your experiences and tips in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more in-depth guides and tutorials related to Raspberry Pi and remote access technologies.
Sources: